〠Instrument R&D 】Ma Xiulian's team at Shenyang National Research Center for Materials Science, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered topological domains and periodic half-child lattices in the ferroelectric oxide materials. This discovery is another major breakthrough in the topological domain structure of ferroelectric materials after the flux is fully closed (Science 2015), adding new substantive content to the structural characteristics analogous to ferromagnetic materials. It also provides new ideas for exploring high-density information storage devices based on ferroelectric materials.
Ferroelectric material refers to a type of material with ferroelectric effect, which is a branch of pyroelectric material. Ferroelectric materials and their applications have become one of the hot research topics in the field of condensed matter physics and solid electronics. The reason for the crystals is that they have quite excellent properties. Many electro-optic crystals and piezoelectric materials are ferroelectric crystals. Ferroelectric crystals have important significance both in technology and theory.
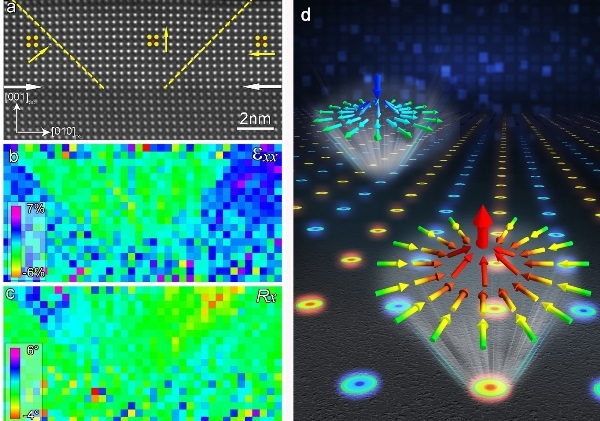
The topological domain structure has topological protection, which can save data for a long time, and has important application value in non-volatile information storage. However, the topological domains in ferroelectric materials generally contain continuous polarization rotations that are not allowed by body symmetry. How to break through the mutual restraint between ferroelectric polarization and lattice strain, realize the effective regulation of polarization reversal and lattice strain, and obtain the structural unit that is expected to be used for ultra-high density information storage is a basic faced in the field of ferroelectric materials today. Scientific puzzles.
All ferroelectric materials are both ferroelectric and piezoelectric. Ferroelectricity means that the material will produce spontaneous polarization within a certain temperature range. Since the positive and negative charge centers in the ferroelectric lattice do not coincide, even without an external electric field, an electric dipole moment can be generated, and its spontaneous polarization can change direction under the action of an external electric field [4]. When the temperature is higher than a certain critical value, its lattice structure changes, the positive and negative charge centers coincide, and the spontaneous polarization disappears. This critical temperature value is called the Curie temperature (Tc). Piezoelectricity is a property that realizes the conversion between mechanical energy and electrical energy. If an external force is applied to the material in a certain direction to deform the material, polarization will occur inside it and a charge will be generated on the surface, which is the piezoelectric effect; on the contrary, if an electric field is applied to the material, the material will deform and produce a mechanical force, which It is the reverse piezoelectric effect. All ferroelectric materials have the above two characteristics, which is one of the material foundations for building electromechanical systems.
After long-term academic accumulation, the research team has made breakthroughs in solving the above basic scientific problems in recent years. They have implemented strain regulation to construct a series of ultrathin ferroelectric PbTiO3/SrTiO3 multilayer films on scandate substrates. Using aberration-corrected electron microscopy with atomic scale resolution, not only found flux fully closed domains Structure and its novel atomic configuration map, and a large-scale periodic array composed of alternating arrangement of clockwise and counterclockwise closed structures was observed (Science 2015). On this basis, scientists at the University of California, Berkeley discovered the ferroelectric vortex domain array in the PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice system with the same composition and different strain conditions using the same electron microscopy method (Nature 2016) ; Team member Tang Yunlong discovered the polarized lattice crystal lattice in PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice during his visit to Berkeley National Laboratory in the United States from 2017 to 2019 (Nature 2019).
The halfton is a non-planar topological domain structure with a topological charge of ±1/2. The discovery of periodic half-child lattices in ferroelectric materials is based on the previous strain control method, the aberration-corrected electron microscopy imaging combined with phase field simulation makes the out-of-plane polarization unique to the half-child structure Presented in real space together with in-plane polarization. They found not only in-plane convergent and in-plane divergent halons in the ultra-thin PbTiO3 thin film (5nm) epitaxially grown on SmScO3 substrates, but also found the inverse half-branch structure and the annihilation after the combination of half-branch and inverse half-branch The domain structure with a topological charge of zero is formed. Through quantitative analysis of ion displacement in the aberration-corrected microscopic images, it was found that the half-sons and anti-half-sons form lattices according to a certain rule (convergent half-sons form a two-dimensional periodic square lattice of 8 nm×8 nm). Phase field simulations show that the formation of half-child lattice is beneficial to reduce the elastic energy of the system, so that the model containing half-child lattice has lower energy than the randomly distributed half-child model.
Quasiparticle is a kind of quantum energy, which exists in a crystal lattice or other interacting particle system. In condensed matter physics, it is very important to introduce such a "quasi-particle" concept.
The concept of quasiparticles was first introduced by Landau in his fluid quantum theory, which is an important concept of solid quantum theory and has gradually developed into meta-excited physics.
The concept of quasiparticles originated from the study of solid state physics. In solid physics, due to the strong interaction between the atoms, it is very difficult to solve the thermodynamic quantities of the system directly from the atomic system using independent particle statistics. If the 3N vibration degrees of freedom of N atoms in a solid are transformed into 3N nearly independent normal vibrations, and the excitation quantum of the normal vibrations is regarded as a kind of "quasi-particle"-phonon, then the strong mutual The atomic system of action is reduced to a "quasi-particle" system (sometimes called "quasi-particle" ideal gas), which greatly simplifies the problem. Here, the concept of "quasi-particle" is given and used.
This work further improves the importance and effectiveness of adjusting the topological domain structure of ferroelectric materials through mismatched strains, and reveals that the electric dipole in the polarized system has a quasi-particle behavior similar to a special condensed structure under certain conditions. It is of great significance to explore high-density nonvolatile information storage devices based on ferroelectric materials. At the same time, the new ferroelectric topological domains can be presented in an intuitive form in real space, which shows that aberration-corrected electron microscopy with sub-angstrom resolution capability and quantitative analysis based on this are scientists' understanding of the structure of matter and the laws of nature Powerful means.
Source: Encyclopedia, Institute of Metal Research
PVC Edge Banding For Furniture
The main function of the edge banding is to seal the cross-section of the board, so as to avoid the damage of the board and the adverse factors (mainly moisture) in the process of use and prevent the formaldehyde inside the board from volatilizing, and at the same time achieve the effect of beautiful decoration.
The product has the following main features: smooth surface, no blistering, no ribbing, moderate gloss, smooth surface and back surface, uniform thickness, uniform width, reasonable hardness, high elasticity, good quality, strong wear resistance, trimmed and sealed The color of the side and the side is close to the surface color, not whitish, good gloss, and the overall color of the finished furniture is coordinated.
Furniture edge banding is a material for protecting, decorating and beautifying the section of furniture panels. It can make a piece of furniture show the overall effect of clear wood grain and colorful.
PVC furniture edge banding is relatively light, which is relative to metal and plexiglass. The reason for the lightness is not because it is a polymer compound, but because they are organic compounds, which are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and chlorine. And other lighter elements.
The material of pvc furniture edge banding is plastic, which is easy to process. Plastic has plasticity, that is, it deforms after heating or pressurizing, and maintains its original shape after the temperature drops or the pressure disappears. It can be processed into edge bands of their respective shapes by extrusion and other methods, such as T-shaped edge bands, H-shaped edge bands, D-shaped edge bands, V-shaped edge bands, I-shapes, and so on.
pvc furniture edge banding is of high quality and low price, and the price of plastic is far less than that of metal.
